Products and services are the lifeblood of your company, but managing them takes work. Product portfolios help us do so effectively, but what is a product portfolio, and how do companies use them? This article will provide insight into product portfolios, their benefits, real-world examples, and how they can help you develop an optimal product portfolio strategy that drives growth.
What Is a Product Portfolio?
A product portfolio is the collection of products or services a company offers. It encompasses every product within the company’s range and can be crucial in guiding strategic decisions.
A well-organized product portfolio helps stakeholders understand each product line’s breadth, depth, and relative value. It provides a high-level overview of the products, their market positioning, and their contribution to the company’s business goals.
The information contained in a portfolio offers several benefits for product leaders, including:
- Strategic Decision-Making Support: It provides a holistic view of the company’s offerings and their performance, guiding resource allocation, product prioritization, and market positioning decisions.
- Risk Mitigation: Examining your products and services from this holistic perspective helps organizations to diversify, minimizing the risk associated with relying too heavily on a single product or market segment.
- Resource Optimization: Analyzing the portfolio helps leaders identify opportunities, allowing for resource reallocation to high-potential areas.
- Enablement of a Customer-Centric Approach: With a better understanding of the product lineup, leaders can align products with target markets, driving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Growth Potential Identification: The portfolio facilitates deep analysis, empowering organizations to identify market gaps, launch new products, and expand into new segments.
Product Portfolio Resource Allocation Examples:
To illustrate the concept, let’s look at an example of how a company could assess allocation in real time across product portfolio dimensions and levels. Here is a snapshot of a portfolio in Dragonboat to help you visualize the structure and organization. Businesses can streamline their decision-making processes and optimize their resource allocation by strategically categorizing their products and aligning them with market segments.
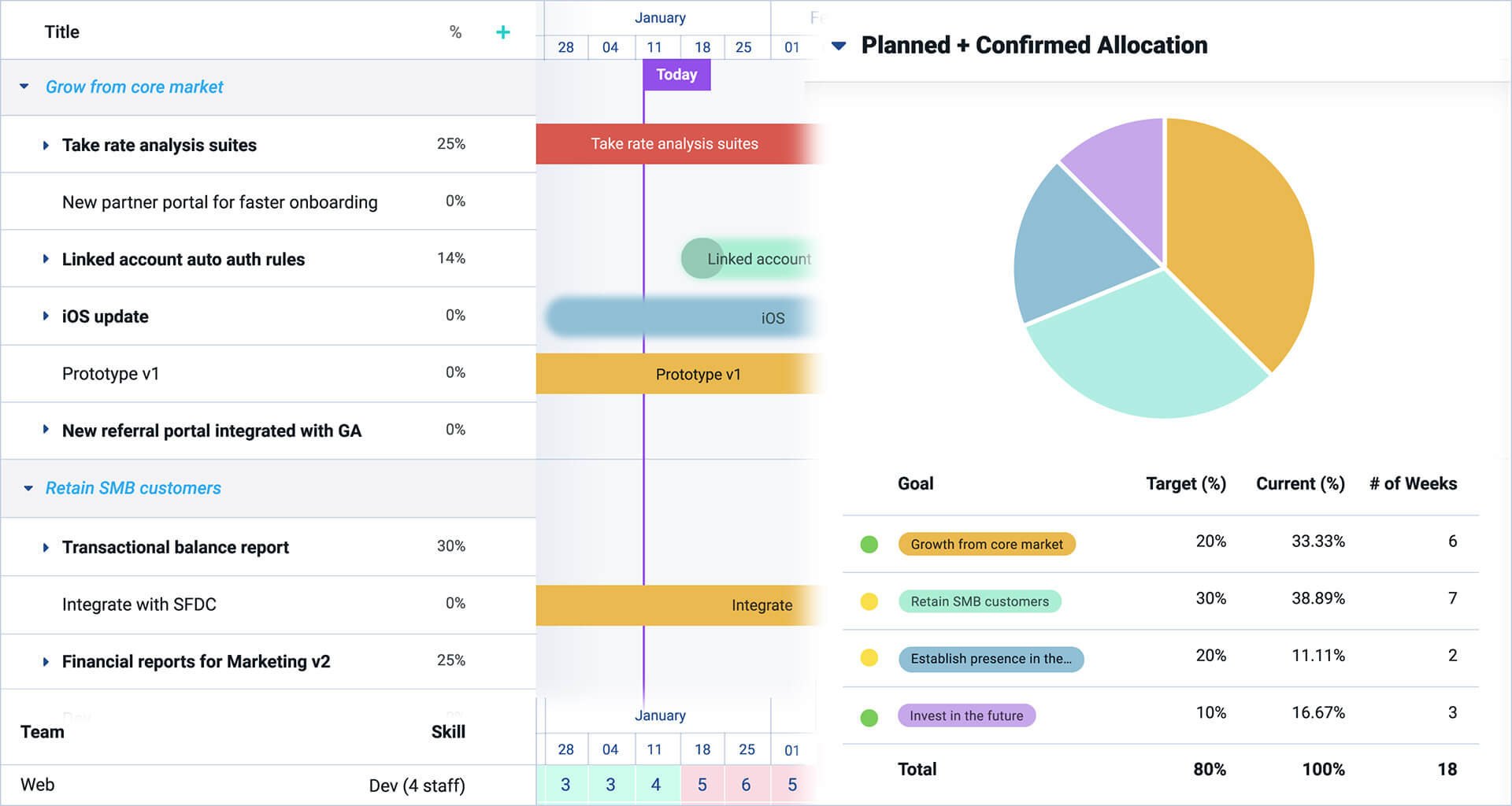
How Do Companies Use Product Portfolios?
Companies utilize product portfolios in various ways to inform critical decisions and drive growth.
For example, by doing a product portfolio analysis, companies can assess the performance of individual products and identify trends. The research might reveal situations that require attention due to products with a high relative market share or lackluster profit margins, informing strategic choices. They could then use the product portfolio to share this information with stakeholders, including investors, partners, and internal teams.
Product Portfolios at Mature vs. Growth Companies
One point to remember is that product portfolios at mature and high-growth companies may differ. In mature companies, the portfolio is typically more extensive and diversified, reflecting a wide range of established products that have gained market acceptance. These portfolios often focus on:
- Optimizing existing products.
- Maximizing profitability.
- Maintaining market share.
In contrast, portfolios at growth companies tend to be more dynamic and agile, characterized by:
- Higher emphasis on innovation.
- New product development.
- Market expansion.
Growth companies may have a narrower portfolio geared towards capturing new market opportunities and driving rapid growth. They may focus on scaling successful products, experimenting with new offerings, and capitalizing on emerging trends. While mature companies prioritize long-term stability and optimizing existing revenue streams, growth companies prioritize agility and creating new revenue streams.
Frameworks to Manage Product Portfolios Effectively
Companies can use Product Portfolio Management (PPM) frameworks to guide their strategic decision-making process.
Such frameworks are valuable for evaluating and managing portfolios effectively, making strategic decisions, and allocating resources to maximize cash flow and impact. But it is important to know their limitations because different frameworks empower you to analyze your portfolio from different viewpoints.
An example framework is Responsive PPM (Responsive Product Portfolio Management). RPPM empowers companies with proactive decision-making for optimal performance. RPPM is an agile practice that involves adapting a company’s portfolio to align with market dynamics and business strategies, enabling organizations to stay responsive and competitive in a rapidly changing business landscape.
The Bottom Line:
A well-structured and data-driven product portfolio is vital for companies seeking to manage their offerings effectively and make informed decisions. It enables them to align business priorities with customer needs, optimize resource allocation, and increase growth rates.
Many find using product portfolio management tools like Dragonboat to organize their portfolio and streamline communication beneficial. With Dragonboat, you can centralize your product data, collaborate seamlessly, and gain actionable insights to propel your business forward.
Are you ready to take control of your product portfolio? Book a demo with Dragonboat today and discover how our powerful platform can transform your product management process.



