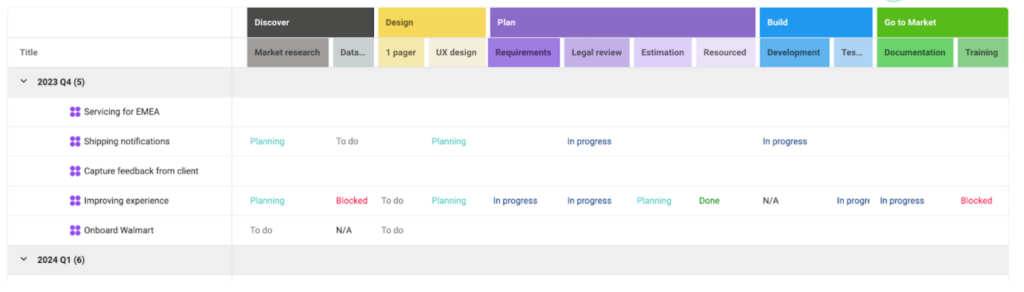
What is the Product Development Life Cycle (PDLC)?
The Product Development Life Cycle (PDLC) is how your organization takes products from initial idea to market launch and beyond. Every company has a PDLC—whether formally documented or organically evolved. It encompasses the stages of product development, including research, planning, design, testing, launch, and optimization to ensure products are built efficiently and aligned with customer and business needs.
PDLCs vary significantly across organizations based on industry, product type, company size, and operational preferences. There is no single correct way to structure a PDLC. What matters is that the organization has a common understanding of how work flows and a single source of truth for the data and context surrounding that work.
Common Elements of the Product Development Life Cycle
PDLC covers the full set of activities from research, planning, to development, product launch, support and optimization to build products that meet business goals and satisfy customer needs. Companies and teams often adjust based on their market, customer, type of product and how they operate.
While the specific stages vary by organization, PDLCs typically include activities across these areas:
- Understanding market opportunities and customer needs
- Planning and validating concepts
- Designing and prototyping solutions
- Building and iterating on products
- Testing with users and refining based on feedback
- Launching and enabling customer adoption
- Monitoring performance and optimizing over time
How these are organized, named, and sequenced depends on your company’s operating model.
Learn more about common Product Development Life Cycle Stages.
Which Teams Are Involved in a PDLC & Who Are the Key Stakeholders?
The PDLC typically involves a cross-functional team, including:
- Product Management: Driving the product vision, strategy, and roadmap.
- Engineering: Developing and building the product.
- Design: Focusing on user interface and user experience.
- Marketing: Promoting the product and acquiring customers.
- Sales: Selling the product to customers.
- Operations: Managing sourcing, manufacturing, and distribution.
- Product Operations: Streamlining and optimizing the product development process.
Key stakeholders include:
- Customers: Providing essential feedback and guidance.
- Executives: Providing strategic direction and allocating resources.
- Investors: Expecting a return on investment.
- Partners: Contributing to the product ecosystem.
Explore more PDLC insights from a Chief Product Officer.
Common Challenges in the PDLC
Every organization faces obstacles when developing new products. Here are some of the biggest challenges:
- Misalignment Between Teams – Lack of communication between product, engineering, marketing, and sales can slow progress.
- Feature Creep – Adding too many features without clear prioritization can delay launches and bloat the product.
- Inefficient Resource Allocation – Poor planning can lead to wasted development time and budget overruns.
- Slow Time-to-Market – Long development cycles may cause organizations to miss market opportunities.
- Ignoring Customer Feedback – Without a customer-driven approach, products may fail to meet user expectations.
Product Development Life Cycle Examples
Different organizations follow different approaches to product development. Companies often adapt or combine approaches based on their needs, and processes evolve over time.
Here’s a breakdown of some common examples:
| Outcome-Focused Product Development Life Cycle (oPDLC) | Aligns product development with business and customer impact, ensuring continuous iteration based on measurable success. |
| Agile Product Development Life Cycle | Iterative development, frequent releases, strong feedback loops. |
| Waterfall Product Development Life Cycle | Linear, stage-by-stage approach with minimal flexibility.
|
| Lean Product Development Life Cycle | Quick experimentation, validated learning, MVP-first approach. |
| Stage-Gate Process | Predefined “gates” where teams evaluate the feasibility before moving forward. |
Common Metrics to Track in the Product Development Life Cycle Process
Common metrics for tracking PDLC performance include:
- Time-to-Market (TTM) – How long it takes to move from ideation to launch.
- Customer Adoption Rate – The percentage of users who adopt the product after launch.
- Feature Engagement Metrics – How often users interact with specific features.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) – Measures customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Development Velocity – Tracks the speed of completing sprints and feature releases
- Churn Rate – The percentage of customers leaving after using the product.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) – The predicted revenue from a long-term customer relationship.
Why These Metrics Matter:
- Help teams optimize development efficiency.
- Identify bottlenecks in the product lifecycle.
- Provide data-driven insights for future product iterations.
Common Challenges in the Product Development Life Cycle
Every organization faces obstacles when developing new products. Here are some of the biggest challenges:
- Misalignment Between Teams – Lack of communication between product, engineering, marketing, and sales can slow progress.
- Feature Creep – Adding too many features without clear prioritization can delay launches and bloat the product.
- Inefficient Resource Allocation – Poor planning can lead to wasted development time and budget overruns.
- Slow Time-to-Market – Long development cycles may cause organizations to miss market opportunities.
- Ignoring Customer Feedback – Without a customer-driven approach, products may fail to meet user expectations.
Product Development Life Cycle Best Practices
- Centralize your PDLC data in a single source of truth accessible to all teams
- Ensure visibility into initiative status, ownership, and progress without manual status reports
- Connect related context—decisions, feedback, dependencies
- Make templates, playbooks, and best practices easily discoverable when teams need them
- Use data-driven decision-making to validate ideas and inform prioritization
- Prioritize customer feedback at every stage to ensure alignment with user needs
- Enable cross-functional collaboration through shared access to the same information
- Leverage automation and AI for faster development cycles and enhanced efficiency.
Discover PDLC for better business outcomes.
Having a Source of Truth PDLC Enables Best Practices and Learning
An easily referable product development lifecycle helps companies minimize risks, optimize resources, and improve market success by enabling everyone easy access to best practices, templates, playbooks, and the current state of product features — enabling faster, better-informed decisions.